Measurements That Matter: Understanding Waist Circumference for Health
Feb 12, 2024 By Madison Evans
In today's health-conscious world, understanding the significance of waist circumference has become paramount. Far beyond a mere measurement, your waist circumference holds vital clues about your overall health and well-being.
As we delve into the complexities of abdominal obesity and its implications, we uncover the importance of accurate measurement techniques and their invaluable insights into our body composition and potential health risks.
Importance of Waist Circumference
Your waist circumference isn't just a number; it can provide valuable clues about your health status. Unlike weighing scales that only tell you about your overall weight, measuring your waist circumference gives you insights into your body composition and distribution of fat.
Excess fat around the waistline, also known as abdominal or visceral fat, is linked to various health risks. People with larger waist circumferences are more prone to developing serious health conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. This type of fat is not just a cosmetic concern; it can actively contribute to inflammation and insulin resistance in the body.
How to Measure Waist Circumference?
Measuring your waist circumference is a straightforward process you can easily perform at home. All you need is a flexible measuring tape and a few minutes of your time. Here's a detailed guide on how to measure your waist circumference accurately:
Prepare for Measurement: Stand up straight in a comfortable position and allow yourself to breathe naturally. Maintaining a relaxed posture throughout the measurement process is essential to ensure accurate results.
Find the Narrowest Part of Your Waist: Find the narrowest point of your waist, usually above your belly button and below your ribcage. It's where your torso naturally curves inward.
Wrap the Measuring Tape: Wrap the measuring tape around your waistline, ensuring it is parallel to the floor. Position the tape snugly against your skin, but be careful not to pull it too tightly, as this may distort the measurement.
Ensure Proper Alignment: The measuring tape is positioned evenly around your waist without twisting or bunching. It should be snug enough to stay in place but not so tight that it digs into your skin or affects your breathing.
Take the Measurement: Once the measuring tape is securely placed, measure in either inches or centimeters, depending on your preference. Read the measurement where the end of the tape meets the rest of the tape measure.
Avoid Holding Your Breath or Sucking In Your Stomach: It's important to maintain normal breathing patterns and avoid sucking in your stomach while taking the measurement. Holding your breath or altering your posture can lead to inaccurate results.
Record the Measurement: Once you have taken the measurement, record the number for future reference. You may want to keep track of your waist circumference measurements over time to monitor changes in your body composition.
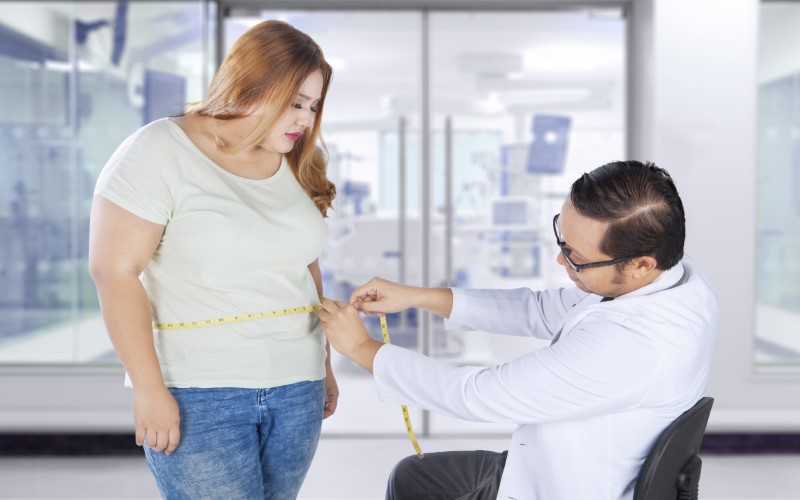

Interpreting the Results
Interpreting the results of your waist circumference measurement is crucial for understanding your risk of developing health issues related to abdominal obesity. While the general guideline for increased health risks is a waist circumference of more than 35 inches (88 cm) for women and 40 inches (102 cm) for men, it's essential to consider individual factors and consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Here are some key points to consider when interpreting your waist circumference measurement:
Body Mass Index (BMI): Waist circumference measurements should be considered in conjunction with BMI, a measure of body fat based on height and weight. Individuals with a high BMI and a large waist circumference may have a higher risk of obesity-related health conditions than those with a high BMI but a smaller waist circumference.
Health Screening: If your waist circumference falls within the high-risk range, consider scheduling a comprehensive health screening with your healthcare provider. This may include blood tests to assess cholesterol levels, blood sugar levels, and other markers of metabolic health, as well as a thorough assessment of your overall health status.

Factors Affecting Waist Circumference
Waist circumference, a key indicator of health, can be influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors can help explain why individuals may have different waist measurements and how they can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy waistline.
Here's an in-depth exploration of the factors affecting waist circumference:
Genetics:
Your genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining your body shape and where you tend to store fat. Some people may have a genetic predisposition to carry excess weight around their midsection, leading to a larger waist circumference even with healthy lifestyle habits.
Lifestyle Choices:
Lifestyle habits such as physical activity levels, dietary patterns, and stress management can greatly impact waist circumference. A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by prolonged periods of sitting and minimal physical activity, can contribute to visceral fat accumulation around the waist. Conversely, regular exercise and movement can help maintain a healthy waistline by burning calories and promoting overall fat loss.
Dietary Habits:
The types of foods you consume and your eating habits can influence your waist circumference. Diets high in processed foods, sugary beverages, and unhealthy fats can contribute to weight gain and abdominal obesity. On the other hand, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support weight management and help reduce waist size.
Body Composition:
Fat and muscle distribution throughout your body also affects your waist circumference. Individuals with higher muscle mass tend to have a lower percentage of body fat and may have smaller waist measurements, even if they weigh more overall. Conversely, those with a higher body fat percentage, especially around the abdomen, may have larger waist circumferences.
Stress Levels:
Chronic stress can impact hormone levels, particularly cortisol, associated with abdominal fat accumulation. High-stress levels can lead to emotional eating, poor sleep quality, and disruptions in appetite regulation, all of which can contribute to weight gain and increased waist circumference over time.
Conclusion
The journey through waist circumference has shed light on its profound impact on health. With knowledge about measuring techniques, interpretation of results, and factors influencing waist size, individuals are empowered to make informed decisions regarding their well-being.
By recognizing the importance of maintaining a healthy waistline and adopting lifestyle modifications conducive to optimal health, we pave the way for a future characterized by vitality and longevity.

Easy Pool Workouts For Quick Fat Burn
Home Gardening Made Easy: Benalla’s Guide to Growing Your Own Produce
How Can You Treat Hypertrophic Scars Effectively?

Essential Guide to Resuming Exercise Postpartum with Assurance and Vigor

Mastering the Art of Foot Care: Using a Pumice Stone for Soft Feet

Bananas and Weight Loss: Unraveling the Truth Behind the Myth

Best Lower Body Superset Workout

Meditation in Motion: Ways to Find Peace Without Sitting Still

An Overview of Fitness Trends: Navigating a Healthier Tomorrow

Discovering Squat Variations: 7 Alternatives to Barbell Squats

Do Lactic Acid Buildups Cause Post-Workout Muscle Soreness?
